Augustus De Morgan
| Augustus De Morgan | |
|---|---|
 Augustus De Morgan (1806-1871)
|
|
| Born | 27 June 1806 Madurai, Madras Presidency, British Raj (now India) |
| Died | 18 March 1871 (aged 64) London, England |
| Residence | |
| Nationality | |
| Fields | Mathematician and logician |
| Institutions | University College London University College School |
| Alma mater | Trinity College University of Cambridge |
| Academic advisors | John Philips Higman George Peacock William Whewell |
| Notable students | Edward Routh James Joseph Sylvester Frederick Guthrie William Stanley Jevons Ada Lovelace Francis Guthrie Stephen Joseph Perry |
| Known for | De Morgan's laws De Morgan algebra Relation algebra Universal algebra |
| Influences | George Boole |
| Influenced | Thomas Corwin Mendenhall |
|
Notes
He was the father of William De Morgan. |
|
Augustus De Morgan (27 June 1806 – 18 March 1871) was a British mathematician and logician. He formulated De Morgan's laws and introduced the term mathematical induction, making its idea rigorous.[1] The crater De Morgan on the Moon is named after him.
Contents |
Biography
Childhood
Augustus De Morgan was born in 1806.[2] His father was Col. Augustus De Morgan, who held various appointments in the service of the East India Company. His mother descended from James Dodson, who computed a table of anti-logarithms, that is, the numbers corresponding to exact logarithms. Augustus De Morgan became blind in one eye a month or two after he was born. The family moved to England when Augustus was seven months old. As his father and grandfather had both been born in India, De Morgan used to say that he was neither English, nor Scottish, nor Irish, but a Briton "unattached", using the technical term applied to an undergraduate of Oxford or Cambridge who is not a member of any one of the Colleges.
When De Morgan was ten years old, his father died. Mrs. De Morgan resided at various places in the southwest of England, and her son received his elementary education at various schools of no great account. His mathematical talents went unnoticed until he was fourteen, when a family-friend discovered him making an elaborate drawing of a figure in Euclid with ruler and compasses. She explained the aim of Euclid to Augustus, and gave him an initiation into demonstration.
He received his secondary education from Mr. Parsons, a Fellow of Oriel College, Oxford, who appreciated classics better than mathematics. His mother was an active and ardent member of the Church of England, and desired that her son should become a clergyman; but by this time De Morgan had begun to show his non-conforming disposition.
University education
In 1823, at the age of sixteen, he entered Trinity College, Cambridge,[3] where he came under the influence of George Peacock and William Whewell, who became his life-long friends; from the former he derived an interest in the renovation of algebra, and from the latter an interest in the renovation of logic—the two subjects of his future life work. His Cambridge tutor was John Philips Higman.
At college the flute, on which he played exquisitely, was his recreation. He was prominent in the musical clubs. His love of knowledge for its own sake interfered with training for the great mathematical race; as a consequence he came out fourth wrangler. This entitled him to the degree of Bachelor of Arts; but to take the higher degree of Master of Arts and thereby become eligible for a fellowship it was then necessary to pass a theological test. To the signing of any such test De Morgan felt a strong objection, although he had been brought up in the Church of England. In about 1875 theological tests for academic degrees were abolished in the Universities of Oxford and Cambridge.
London University
As no career was open to him at his own university, he decided to go to the Bar, and took up residence in London; but he much preferred teaching mathematics to reading law. About this time the movement for founding London University (now University College London) took shape. The two ancient universities of Oxford and Cambridge were so guarded by theological tests that no Jew or Dissenter outside the Church of England could enter as a student, still less be appointed to any office. A body of liberal-minded men resolved to meet the difficulty by establishing in London a University on the principle of religious neutrality. De Morgan, then 22 years of age, was appointed Professor of Mathematics. His introductory lecture "On the study of mathematics" is a discourse upon mental education of permanent value which has been recently reprinted in the United States.
The London University was a new institution, and the relations of the Council of management, the Senate of professors and the body of students were not well defined. A dispute arose between the professor of anatomy and his students, and in consequence of the action taken by the Council, several professors resigned, headed by De Morgan. Another professor of mathematics was appointed, who then drowned a few years later. De Morgan had shown himself a prince of teachers: he was invited to return to his chair, which thereafter became the continuous centre of his labours for thirty years.
The same body of reformers—headed by Lord Brougham, a Scotsman eminent both in science and politics who had instituted the London University—founded about the same time a Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge. Its object was to spread scientific and other knowledge by means of cheap and clearly written treatises by the best writers of the time. One of its most voluminous and effective writers was De Morgan. He wrote a great work on The Differential and Integral Calculus which was published by the Society; and he wrote one-sixth of the articles in the Penny Cyclopedia, published by the Society, and issued in penny numbers. When De Morgan came to reside in London he found a congenial friend in William Frend, notwithstanding his mathematical heresy about negative quantities. Both were arithmeticians and actuaries, and their religious views were somewhat similar. Frend lived in what was then a suburb of London, in a country-house formerly occupied by Daniel Defoe and Isaac Watts. De Morgan with his flute was a welcome visitor; and in 1837 he married Sophia Elizabeth, one of Frend's daughters.
The London University of which De Morgan was a professor was a different institution from the University of London. The University of London was founded about ten years later by the Government for the purpose of granting degrees after examination, without any qualification as to residence. The London University was affiliated as a teaching college with the University of London, and its name was changed to University College. The University of London was not a success as an examining body; a teaching University was demanded. De Morgan was a highly successful teacher of mathematics. It was his plan to lecture for an hour, and at the close of each lecture to give out a number of problems and examples illustrative of the subject lectured on; his students were required to sit down to them and bring him the results, which he looked over and returned revised before the next lecture. In De Morgan's opinion, a thorough comprehension and mental assimilation of great principles far outweighed in importance any merely analytical dexterity in the application of half-understood principles to particular cases.
During this period, he also promoted the work of self-taught Indian mathematician Ramchundra, who has been called De Morgan's Ramanujam. He supervised the publication in London of Ramchundra's book on "Maxima and Minima" in 1859. In the introduction to this book, he acknowledged being aware of the Indian tradition of logic, although we don't know if this had any influence on his own work.
De Morgan had three sons and four daughters. His eldest son was the potter William De Morgan. His second son George acquired great distinction in mathematics both at University College and the University of London. He and another like-minded alumnus conceived the idea of founding a Mathematical Society in London, where mathematical papers would be not only received (as by the Royal Society) but actually read and discussed. The first meeting was held in University College; De Morgan was the first president, his son the first secretary. It was the beginning of the London Mathematical Society.
Retirement and death
In 1866 the chair of mental philosophy in University College fell vacant. James Martineau, a Unitarian clergyman and professor of mental philosophy, was recommended formally by the Senate to the Council; but in the Council there were some who objected to a Unitarian clergyman, and others who objected to theistic philosophy. A layman of the school of Bain and Spencer was appointed. De Morgan considered that the old standard of religious neutrality had been hauled down, and forthwith resigned. He was now 60 years of age. His pupils secured him a pension of £500p.a., but misfortunes followed. Two years later his son George – the "younger Bernoulli", as Augustus loved to hear him called, in allusion to the eminent father and son mathematicians of that name – died. This blow was followed by the death of a daughter. Five years after his resignation from University College De Morgan died of nervous prostration on 18 March 1871.
Mathematical work
De Morgan was a brilliant and witty writer, whether as a controversialist or as a correspondent. In his time there flourished two Sir William Hamiltons who have often been confounded. The one was Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet (that is, his title was inherited), a Scotsman, professor of logic and metaphysics at the University of Edinburgh; the other was a knight (that is, won the title), an Irishman, professor at astronomy in the University of Dublin. The baronet contributed to logic, especially the doctrine of the quantification of the predicate; the knight, whose full name was William Rowan Hamilton, contributed to mathematics, especially geometric algebra, and first described the Quaternions. De Morgan was interested in the work of both, and corresponded with both; but the correspondence with the Scotsman ended in a public controversy, whereas that with the Irishman was marked by friendship and terminated only by death. In one of his letters to Rowan, De Morgan says,
- "Be it known unto you that I have discovered that you and the other Sir W. H. are reciprocal polars with respect to me (intellectually and morally, for the Scottish baronet is a polar bear, and you, I was going to say, are a polar gentleman). When I send a bit of investigation to Edinburgh, the W. H. of that ilk says I took it from him. When I send you one, you take it from me, generalize it at a glance, bestow it thus generalized upon society at large, and make me the second discoverer of a known theorem."
The correspondence of De Morgan with Hamilton the mathematician extended over twenty-four years; it contains discussions not only of mathematical matters, but also of subjects of general interest. It is marked by geniality on the part of Hamilton and by wit on the part of De Morgan. The following is a specimen: Hamilton wrote,
- "My copy of Berkeley's work is not mine; like Berkeley, you know, I am an Irishman."
De Morgan replied,
- "Your phrase 'my copy is not mine' is not a bull. It is perfectly good English to use the same word in two different senses in one sentence, particularly when there is usage. Incongruity of language is no bull, for it expresses meaning. But incongruity of ideas (as in the case of the Irishman who was pulling up the rope, and finding it did not finish, cried out that somebody had cut off the other end of it) is the genuine bull."
De Morgan was full of personal peculiarities. On the occasion of the installation of his friend, Lord Brougham, as Rector of the University of Edinburgh, the Senate offered to confer on him the honorary degree of LL. D.; he declined the honour as a misnomer. He once printed his name: Augustus De Morgan, H - O - M - O - P - A - U - C - A - R - U - M - L - I - T - E - R - A - R - U - M.
He disliked the provinces outside London, and while his family enjoyed the seaside, and men of science were having a good time at a meeting of the British Association in the country he remained in the hot and dusty libraries of the metropolis. He said that he felt like Socrates, who declared that the farther he was from Athens the farther was he from happiness. He never sought to become a Fellow of the Royal Society, and he never attended a meeting of the Society; he said that he had no ideas or sympathies in common with the physical philosopher. His attitude was possibly due to his physical infirmity, which prevented him from being either an observer or an experimenter. He never voted at an election, and he never visited the House of Commons, or the Tower of London, or Westminster Abbey.
Were the writings of De Morgan published in the form of collected works, they would form a small library, for example his writings for the Useful Knowledge Society. Mainly through the efforts of Peacock and Whewell, a Philosophical Society had been inaugurated at Cambridge; and to its Transactions De Morgan contributed four memoirs on the foundations of algebra, and an equal number on formal logic. The best presentation of his view of algebra is found in a volume, entitled Trigonometry and Double Algebra, published in 1849; and his earlier view of formal logic is found in a volume published in 1847. His most distinctive work is styled a Budget of Paradoxes; it originally appeared as letters in the columns of the Athenæum journal; it was revised and extended by De Morgan in the last years of his life, and was published posthumously by his widow.
George Peacock's theory of algebra was much improved by D. F. Gregory, a younger member of the Cambridge School, who laid stress not on the permanence of equivalent forms, but on the permanence of certain formal laws. This new theory of algebra as the science of symbols and of their laws of combination was carried to its logical issue by De Morgan; and his doctrine on the subject is still followed by English algebraists in general. Thus George Chrystal founds his Textbook of Algebra on De Morgan's theory; although an attentive reader may remark that he practically abandons it when he takes up the subject of infinite series. De Morgan's theory is stated in his volume on Trigonometry and Double Algebra. In the chapter (of the book) headed "On symbolic algebra" he writes:
- "In abandoning the meaning of symbols, we also abandon those of the words which describe them. Thus addition is to be, for the present, a sound void of sense. It is a mode of combination represented by
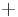 ; when
; when 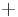 receives its meaning, so also will the word addition. It is most important that the student should bear in mind that, with one exception, no word nor sign of arithmetic or algebra has one atom of meaning throughout this chapter, the object of which is symbols, and their laws of combination, giving a symbolic algebra which may hereafter become the grammar of a hundred distinct significant algebras. If any one were to assert that
receives its meaning, so also will the word addition. It is most important that the student should bear in mind that, with one exception, no word nor sign of arithmetic or algebra has one atom of meaning throughout this chapter, the object of which is symbols, and their laws of combination, giving a symbolic algebra which may hereafter become the grammar of a hundred distinct significant algebras. If any one were to assert that 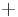 and
and 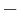 might mean reward and punishment, and
might mean reward and punishment, and  ,
,  ,
,  , etc., might stand for virtues and vices, the reader might believe him, or contradict him, as he pleases, but not out of this chapter. The one exception above noted, which has some share of meaning, is the sign
, etc., might stand for virtues and vices, the reader might believe him, or contradict him, as he pleases, but not out of this chapter. The one exception above noted, which has some share of meaning, is the sign  placed between two symbols as in
placed between two symbols as in 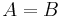 . It indicates that the two symbols have the same resulting meaning, by whatever steps attained. That
. It indicates that the two symbols have the same resulting meaning, by whatever steps attained. That  and
and  , if quantities, are the same amount of quantity; that if operations, they are of the same effect, etc."
, if quantities, are the same amount of quantity; that if operations, they are of the same effect, etc."
- Here, it may be asked, why does the symbol
 prove refractory to the symbolic theory? De Morgan admits that there is one exception; but an exception proves the rule, not in the usual but illogical sense of establishing it, but in the old and logical sense of testing its validity. If an exception can be established, the rule must fall, or at least must be modified. Here I am talking not of grammatical rules, but of the rules of science or nature.
prove refractory to the symbolic theory? De Morgan admits that there is one exception; but an exception proves the rule, not in the usual but illogical sense of establishing it, but in the old and logical sense of testing its validity. If an exception can be established, the rule must fall, or at least must be modified. Here I am talking not of grammatical rules, but of the rules of science or nature.
De Morgan proceeds to give an inventory of the fundamental symbols of algebra, and also an inventory of the laws of algebra. The symbols are 0, 1, +, −, ×, ÷, ()(), and letters; these only, all others are derived. His inventory of the fundamental laws is expressed under fourteen heads, but some of them are merely definitions. The laws proper may be reduced to the following, which, as he admits, are not all independent of one another:
- Law of signs. + + = +, + − = −, − + = −, − − = +, × × = ×, × ÷ = ÷, ÷ × = ÷, ÷ ÷ = ×.
- Commutative law. a+b = b+a, ab=ba.
- Distributive law. a(b+c) = ab+ac.
- Index laws. ab×ac=ab+c, (ab)c=abc, (ab)d= ad×bd.
- a−a=0, a÷a=1.
The last two may be called the rules of reduction. De Morgan professes to give a complete inventory of the laws which the symbols of algebra must obey, for he says, "Any system of symbols which obeys these laws and no others, except they be formed by combination of these laws, and which uses the preceding symbols and no others, except they be new symbols invented in abbreviation of combinations of these symbols, is symbolic algebra." From his point of view, none of the above principles are rules; they are formal laws, that is, arbitrarily chosen relations to which the algebraic symbols must be subject. He does not mention the law, which had already been pointed out by Gregory, namely, 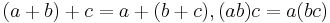 and to which was afterwards given the name of the law of association. If the commutative law fails, the associative may hold good; but not vice versa. It is an unfortunate thing for the symbolist or formalist that in universal arithmetic
and to which was afterwards given the name of the law of association. If the commutative law fails, the associative may hold good; but not vice versa. It is an unfortunate thing for the symbolist or formalist that in universal arithmetic 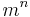 is not equal to
is not equal to 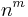 ; for then the commutative law would have full scope. Why does he not give it full scope? Because the foundations of algebra are, after all, real not formal, material not symbolic. To the formalists the index operations are exceedingly refractory, in consequence of which some take no account of them, but relegate them to applied mathematics. To give an inventory of the laws which the symbols of algebra must obey is an impossible task, and reminds one not a little of the task of those philosophers who attempt to give an inventory of the a priori knowledge of the mind.
; for then the commutative law would have full scope. Why does he not give it full scope? Because the foundations of algebra are, after all, real not formal, material not symbolic. To the formalists the index operations are exceedingly refractory, in consequence of which some take no account of them, but relegate them to applied mathematics. To give an inventory of the laws which the symbols of algebra must obey is an impossible task, and reminds one not a little of the task of those philosophers who attempt to give an inventory of the a priori knowledge of the mind.
De Morgan's work entitled Trigonometry and Double Algebra consists of two parts; the former of which is a treatise on Trigonometry, and the latter a treatise on generalized algebra which he calls Double Algebra. The first stage in the development of algebra is arithmetic, where numbers only appear and symbols of operations such as 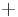 ,
, 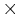 , etc. The next stage is universal arithmetic, where letters appear instead of numbers, so as to denote numbers universally, and the processes are conducted without knowing the values of the symbols. Let
, etc. The next stage is universal arithmetic, where letters appear instead of numbers, so as to denote numbers universally, and the processes are conducted without knowing the values of the symbols. Let 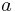 and
and  denote any numbers; then such an expression as
denote any numbers; then such an expression as  may be impossible; so that in universal arithmetic there is always a proviso, provided the operation is possible. The third stage is single algebra, where the symbol may denote a quantity forwards or a quantity backwards, and is adequately represented by segments on a straight line passing through an origin. Negative quantities are then no longer impossible; they are represented by the backward segment. But an impossibility still remains in the latter part of such an expression as
may be impossible; so that in universal arithmetic there is always a proviso, provided the operation is possible. The third stage is single algebra, where the symbol may denote a quantity forwards or a quantity backwards, and is adequately represented by segments on a straight line passing through an origin. Negative quantities are then no longer impossible; they are represented by the backward segment. But an impossibility still remains in the latter part of such an expression as 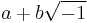 which arises in the solution of the quadratic equation. The fourth stage is double algebra; the algebraic symbol denotes in general a segment of a line in a given plane; it is a double symbol because it involves two specifications, namely, length and direction; and
which arises in the solution of the quadratic equation. The fourth stage is double algebra; the algebraic symbol denotes in general a segment of a line in a given plane; it is a double symbol because it involves two specifications, namely, length and direction; and 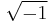 is interpreted as denoting a quadrant. The expression
is interpreted as denoting a quadrant. The expression 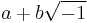 then represents a line in the plane having an abscissa
then represents a line in the plane having an abscissa 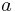 and an ordinate
and an ordinate  . Argand and Warren carried double algebra so far; but they were unable to interpret on this theory such an expression as
. Argand and Warren carried double algebra so far; but they were unable to interpret on this theory such an expression as 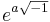 . De Morgan attempted it by reducing such an expression to the form
. De Morgan attempted it by reducing such an expression to the form 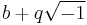 , and he considered that he had shown that it could be always so reduced. The remarkable fact is that this double algebra satisfies all the fundamental laws above enumerated, and as every apparently impossible combination of symbols has been interpreted it looks like the complete form of algebra.
, and he considered that he had shown that it could be always so reduced. The remarkable fact is that this double algebra satisfies all the fundamental laws above enumerated, and as every apparently impossible combination of symbols has been interpreted it looks like the complete form of algebra.
If the above theory is true, the next stage of development ought to be triple algebra and if 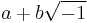 truly represents a line in a given plane, it ought to be possible to find a third term which added to the above would represent a line in space. Argand and some others guessed that it was
truly represents a line in a given plane, it ought to be possible to find a third term which added to the above would represent a line in space. Argand and some others guessed that it was 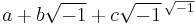 although this contradicts the truth established by Euler that
although this contradicts the truth established by Euler that 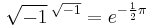 . De Morgan and many others worked hard at the problem, but nothing came of it until the problem was taken up by Hamilton. We now see the reason clearly: the symbol of double algebra denotes not a length and a direction; but a multiplier and an angle. In it the angles are confined to one plane; hence the next stage will be a quadruple algebra, when the axis of the plane is made variable. And this gives the answer to the first question; double algebra is nothing but analytical plane trigonometry, and this is why it has been found to be the natural analysis for alternating currents. But De Morgan never got this far; he died with the belief "that double algebra must remain as the full development of the conceptions of arithmetic, so far as those symbols are concerned which arithmetic immediately suggests."
. De Morgan and many others worked hard at the problem, but nothing came of it until the problem was taken up by Hamilton. We now see the reason clearly: the symbol of double algebra denotes not a length and a direction; but a multiplier and an angle. In it the angles are confined to one plane; hence the next stage will be a quadruple algebra, when the axis of the plane is made variable. And this gives the answer to the first question; double algebra is nothing but analytical plane trigonometry, and this is why it has been found to be the natural analysis for alternating currents. But De Morgan never got this far; he died with the belief "that double algebra must remain as the full development of the conceptions of arithmetic, so far as those symbols are concerned which arithmetic immediately suggests."
When the study of mathematics revived at the University of Cambridge, so did the study of logic. The moving spirit was Whewell, the Master of Trinity College, whose principal writings were a History of the Inductive Sciences, and Philosophy of the Inductive Sciences. Doubtless De Morgan was influenced in his logical investigations by Whewell; but other influential contemporaries were Sir W. Hamilton of Edinburgh, and Professor Boole of Cork. De Morgan's work on Formal Logic, published in 1847, is principally remarkable for his development of the numerically definite syllogism. The followers of Aristotle say that from two particular propositions such as Some M's are A's , and Some M's are B's nothing follows of necessity about the relation of the A's and B's. But they go further and say in order that any relation about the A's and B's may follow of necessity, the middle term must be taken universally in one of the premises. De Morgan pointed out that from Most M's are A's and Most M's are B's it follows of necessity that some A's are B's and he formulated the numerically definite syllogism which puts this principle in exact quantitative form. Suppose that the number of the M's is  , of the M's that are A's is
, of the M's that are A's is 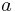 , and of the M's that are B's is
, and of the M's that are B's is  ; then there are at least
; then there are at least 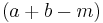 A's that are B's. Suppose that the number of souls on board a steamer was 1000, that 500 were in the saloon, and 700 were lost; it follows of necessity, that at least 700+500-1000, that is, 200, saloon passengers were lost. This single principle suffices to prove the validity of all the Aristotelian moods; it is therefore a fundamental principle in necessary reasoning.
A's that are B's. Suppose that the number of souls on board a steamer was 1000, that 500 were in the saloon, and 700 were lost; it follows of necessity, that at least 700+500-1000, that is, 200, saloon passengers were lost. This single principle suffices to prove the validity of all the Aristotelian moods; it is therefore a fundamental principle in necessary reasoning.
Here then De Morgan had made a great advance by introducing quantification of the terms. At that time Sir W. Hamilton was teaching at Edinburgh a doctrine of the quantification of the predicate, and a correspondence sprang up. However, De Morgan soon perceived that Hamilton's quantification was of a different character; that it meant for example, substituting the two forms The whole of A is the whole of B, and The whole of A is a part of B for the Aristotelian form All A's are B's. Hamilton thought that he had placed the keystone in the Aristotelian arch, as he phrased it; although it must have been a curious arch which could stand 2000 years without a keystone. As a consequence he had no room for De Morgan's innovations. He accused De Morgan of plagiarism, and the controversy raged for years in the columns of the Athenæum, and in the publications of the two writers.
The memoirs on logic which De Morgan contributed to the Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society subsequent to the publication of his book on Formal Logic are by far the most important contributions which he made to the science, especially his fourth memoir, in which he begins work in the broad field of the logic of relatives. This is the true field for the logician of the twentieth century, in which work of the greatest importance is to be done towards improving language and facilitating thinking processes which occur all the time in practical life. Identity and difference are the two relations which have been considered by the logician; but there are many others equally deserving of study, such as equality, equivalence, consanguinity, affinity, etc.
In the introduction to the Budget of Paradoxes De Morgan explains what he means by the word.
- "A great many individuals, ever since the rise of the mathematical method, have, each for himself, attacked its direct and indirect consequences. I shall call each of these persons a paradoxer, and his system a paradox. I use the word in the old sense: a paradox is something which is apart from general opinion, either in subject matter, method, or conclusion. Many of the things brought forward would now be called crotchets, which is the nearest word we have to old paradox. But there is this difference, that by calling a thing a crotchet we mean to speak lightly of it; which was not the necessary sense of paradox. Thus in the 16th century many spoke of the earth's motion as the paradox of Copernicus and held the ingenuity of that theory in very high esteem, and some I think who even inclined towards it. In the seventeenth century the deprivation of meaning took place, in England at least."
How can the sound paradoxer be distinguished from the false paradoxer? De Morgan supplies the following test:
- "The manner in which a paradoxer will show himself, as to sense or nonsense, will not depend upon what he maintains, but upon whether he has or has not made a sufficient knowledge of what has been done by others, especially as to the mode of doing it, a preliminary to inventing knowledge for himself... New knowledge, when to any purpose, must come by contemplation of old knowledge, in every matter which concerns thought; mechanical contrivance sometimes, not very often, escapes this rule. All the men who are now called discoverers, in every matter ruled by thought, have been men versed in the minds of their predecessors and learned in what had been before them. There is not one exception."
- "I remember that just before the American Association met at Indianapolis in 1890, the local newspapers heralded a great discovery which was to be laid before the assembled savants -- a young man living somewhere in the country had squared the circle. While the meeting was in progress I observed a young man going about with a roll of paper in his hand. He spoke to me and complained that the paper containing his discovery had not been received. I asked him whether his object in presenting the paper was not to get it read, printed and published so that everyone might inform himself of the result; to all of which he assented readily. But, said I, many men have worked at this question, and their results have been tested fully, and they are printed for the benefit of anyone who can read; have you informed yourself of their results? To this there was no assent, but the sickly smile of the false paradoxer"
The Budget consists of a review of a large collection of paradoxical books which De Morgan had accumulated in his own library, partly by purchase at bookstands, partly from books sent to him for review, partly from books sent to him by the authors. He gives the following classification: squarers of the circle, trisectors of the angle, duplicators of the cube, constructors of perpetual motion, subverters of gravitation, stagnators of the earth, builders of the universe. You will still find specimens of all these classes in the New World and in the new century. De Morgan gives his personal knowledge of paradoxers.
- "I suspect that I know more of the English class than any man in Britain. I never kept any reckoning: but I know that one year with another? -- and less of late years than in earlier time? -- I have talked to more than five in each year, giving more than a hundred and fifty specimens. Of this I am sure, that it is my own fault if they have not been a thousand. Nobody knows how they swarm, except those to whom they naturally resort. They are in all ranks and occupations, of all ages and characters. They are very earnest people, and their purpose is bona fide, the dissemination of their paradoxes. A great many -- the mass, indeed -- are illiterate, and a great many waste their means, and are in or approaching penury. These discoverers despise one another."
A paradoxer to whom De Morgan paid the compliment which Achilles paid Hector—to drag him round the walls again and again—was James Smith, a successful merchant of Liverpool. He found 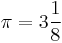 . His mode of reasoning was a curious caricature of the reductio ad absurdum of Euclid. He said let
. His mode of reasoning was a curious caricature of the reductio ad absurdum of Euclid. He said let 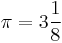 , and then showed that on that supposition, every other value of
, and then showed that on that supposition, every other value of 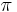 must be absurd; consequently
must be absurd; consequently 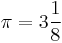 is the true value. The following is a specimen of De Morgan's dragging round the walls of Troy:
is the true value. The following is a specimen of De Morgan's dragging round the walls of Troy:
- "Mr. Smith continues to write me long letters, to which he hints that I am to answer. In his last of 31 closely written sides of note paper, he informs me, with reference to my obstinate silence, that though I think myself and am thought by others to be a mathematical Goliath, I have resolved to play the mathematical snail, and keep within my shell. A mathematical snail! This cannot be the thing so called which regulates the striking of a clock; for it would mean that I am to make Mr. Smith sound the true time of day, which I would by no means undertake upon a clock that gains 19 seconds odd in every hour by false quadrative value of
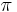 . But he ventures to tell me that pebbles from the sling of simple truth and common sense will ultimately crack my shell, and put me hors de combat. The confusion of images is amusing: Goliath turning himself into a snail to avoid
. But he ventures to tell me that pebbles from the sling of simple truth and common sense will ultimately crack my shell, and put me hors de combat. The confusion of images is amusing: Goliath turning himself into a snail to avoid 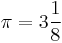 and James Smith, Esq., of the Mersey Dock Board: and put hors de combat by pebbles from a sling. If Goliath had crept into a snail shell, David would have cracked the Philistine with his foot. There is something like modesty in the implication that the crack-shell pebble has not yet taken effect; it might have been thought that the slinger would by this time have been singing -- And thrice [and one-eighth] I routed all my foes, And thrice [and one-eighth] I slew the slain."
and James Smith, Esq., of the Mersey Dock Board: and put hors de combat by pebbles from a sling. If Goliath had crept into a snail shell, David would have cracked the Philistine with his foot. There is something like modesty in the implication that the crack-shell pebble has not yet taken effect; it might have been thought that the slinger would by this time have been singing -- And thrice [and one-eighth] I routed all my foes, And thrice [and one-eighth] I slew the slain."
In the region of pure mathematics De Morgan could detect easily the false from the true paradox; but he was not so proficient in the field of physics. His father-in-law was a paradoxer, and his wife a paradoxer; and in the opinion of the physical philosophers De Morgan himself scarcely escaped. His wife wrote a book describing the phenomena of spiritualism, table-rapping, table-turning, etc.; and De Morgan wrote a preface in which he said that he knew some of the asserted facts, believed others on testimony, but did not pretend to know whether they were caused by spirits, or had some unknown and unimagined origin. From this alternative he left out ordinary material causes. Faraday delivered a lecture on Spiritualism, in which he laid it down that in the investigation we ought to set out with the idea of what is physically possible, or impossible; De Morgan did not believe this.
Relations
De Morgan discovered relation algebra in his Syllabus of a Proposed System of Logic (1966: 208-46), first published in 1860. This algebra was extended by Charles Sanders Peirce (who admired De Morgan and met him shortly before his death), and re-exposited and further extended in vol. 3 of Ernst Schröder's Vorlesungen über die Algebra der Logik. Relation algebra proved critical to the Principia Mathematica of Bertrand Russell and Alfred North Whitehead. In turn, this algebra became the subject of much further work, starting in 1940, by Alfred Tarski and his colleagues and students at the University of California.
Legacy
Beyond his great mathematical legacy, the headquarters of the London Mathematical Society is called De Morgan House and the student society of the Mathematics Department of University College London is called the August De Morgan Society.
Selected writings
- 1836. An Explanation of the Gnomonic Projection of the Sphere. London: Baldwin.
- 1837. Elements of Trigonometry, and Trigonometrical Analysis. London: Taylor & Walton.
- 1837. The Elements of Algebra. London: Taylor & Walton.
- 1838. An Essay on Probabilities. London: Longman, Orme, Brown, Green &Longmans.
- 1840. The Elements of Arithmetic. London: Taylor & Walton.
- 1840. First Notions of Logic, Preparatory to the Study of Geometry. London: Taylor & Walton.
- 1842. The Differential and Integral Calculus. London: Baldwin.
- 1845. The Globes, Celestial and Terrestrial. London: Malby & Co.
- 1847. Formal Logic or The Calculus of Inference. London: Taylor & Walton.
- 1849. Trigonometry and Double Algebra. London: Talyor, Walton & Malbery.
- 1860. Syllabus of a Proposed System of Logic. London: Walton & Malbery.
- 1872. A Budget of Paradoxes New York: Dover.
See also
- De Morgan's laws
- Relation algebra
References and notes
- ↑ De Morgan, (1838) Induction (mathematics), The Penny Cyclopedia.
- ↑ The year of his birth may be found by solving a conundrum proposed by himself, "I was
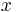 years of age in the year
years of age in the year 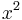 " (He was 43 in 1849). The problem is indeterminate, but it is made strictly determinate by the century of its utterance and the limit to a man's life. Those born in 1892, 1980, and 2070 are similarly privileged.
" (He was 43 in 1849). The problem is indeterminate, but it is made strictly determinate by the century of its utterance and the limit to a man's life. Those born in 1892, 1980, and 2070 are similarly privileged. - ↑ De Morgan, Augustus in Venn, J. & J. A., Alumni Cantabrigienses, Cambridge University Press, 10 vols, 1922–1958.
Further readings
- De Morgan, A., 1966. Logic: On the Syllogism and Other Logical Writings. Heath, P., ed. Routledge. A useful collection of De Morgan's most important writings on logic.
- De Morgan, Sophia Elizabeth (1882). Memoir of Augustus De Morgan. London: Longmans, Green and Company. http://books.google.com/?id=YiGJGOtbMHcC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Augustus+De+Morgan.
- Grattan-Guinness, Ivor (2000). The Search for Mathematical Roots 1870-1940. Princeton University Press.
- Macfarlane, Alexander (1916). Lectures on Ten British Mathematicians of the Nineteenth Century. New York: John Wiley and Sons. http://www.gutenberg.net/etext06/tbmms10p.pdf.
- Merrill, Daniel D. (1990). Augustus De Morgan and the Logic of Relations. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
External links
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Augustus De Morgan", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/De_Morgan.html.
- Papers of Augustus De Morgan held by Senate House Library, University of London
- Library of Augustus De Morgan